Forearm fracture
Pathological fracture of the radius: benign tumour
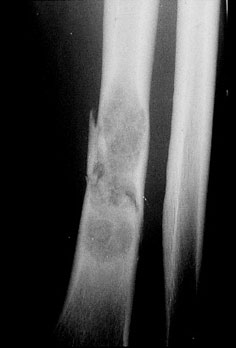 |
|
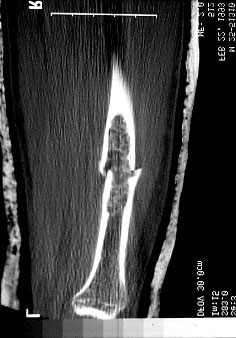 |
|
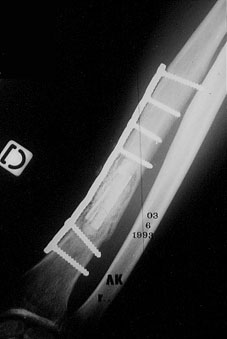
![]()
![]() A long stick of natural coral is placed in the medullary canal, after removal of the tumour.
A long stick of natural coral is placed in the medullary canal, after removal of the tumour.
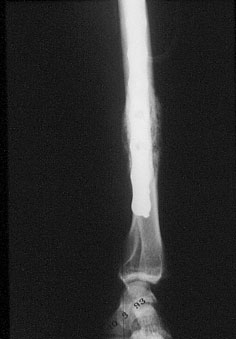
Decortication is done and granules of natural canal are placed around the cortex.
Six months after surgery, the stick is still visible. Cortices are healed.
Osteoporotic close fracture of the lower one/third radius and the lower one/fourth cubitus
Image n° 1: Close fracture of both radius and cubitus.
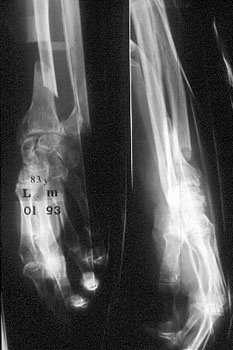 |
|
Image n° 2:
45 days after surgery.
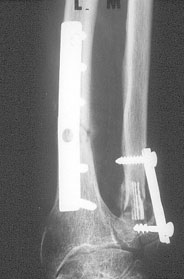 |
|
Image n° 3:
Healing of both forearm bones.
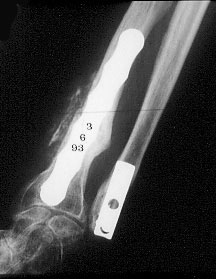
![]()
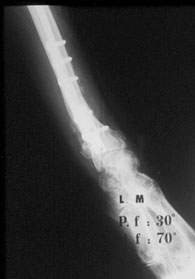
![]() 5 months after surgery the cubitus is nicely rebuilt. Some granules are yet seen along the radius shaft.
5 months after surgery the cubitus is nicely rebuilt. Some granules are yet seen along the radius shaft.
Severe osteoportic comminuted fracture of the wrist
Image n° 1: pre-operative X-rays
![]() This old patient (84 years old) had a severe osteoporotic disease. She broke her hip, lost many centimetres due to multiple fractures of vertebrae. The skin along the cubitus was cut, so she had to be operated in emergency. Note the multiple fragments of both forearm bones.
This old patient (84 years old) had a severe osteoporotic disease. She broke her hip, lost many centimetres due to multiple fractures of vertebrae. The skin along the cubitus was cut, so she had to be operated in emergency. Note the multiple fragments of both forearm bones.
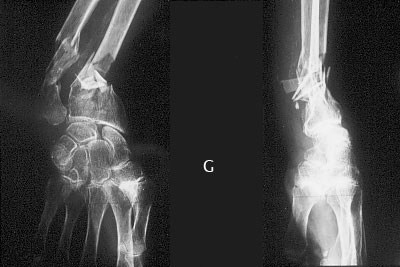
Image n° 2: post-operative X-rays
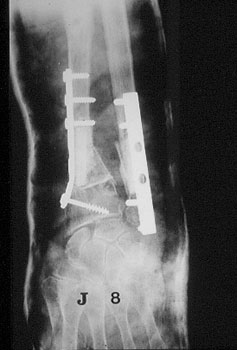 |
|
Image n° 3: X-rays of the healed fractures
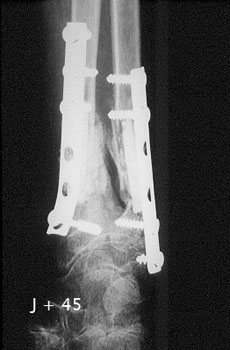
|
|
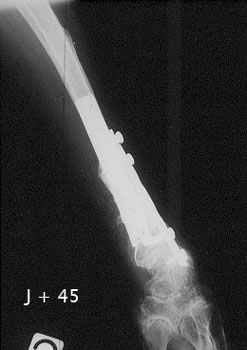 |
Conclusion :
![]() In three cases we used a stick of biomaterial in the medullary canal to have - at first sight - a mechanical effect, before the biological effect occurs in a second time. No dystrophic sympathetic reflex occurred in any case.
In three cases we used a stick of biomaterial in the medullary canal to have - at first sight - a mechanical effect, before the biological effect occurs in a second time. No dystrophic sympathetic reflex occurred in any case.
| Upper Limb pathology: Wrist |